4 Steps to Load Test MongoDB using YCSB workloads on Kubernetes cluster

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
Introduction
In this post, we’ll be creating a Kubernetes cluster and configuring vSphere storage for kubernetes. We shall also deploy dynamic storage provisioning and configure MongoDB applications & run YCSB workloads for database simulations.
Step1: Install a Kubernetes Cluster on ESXi VMs.
Step2: Configure vSphere cloud provider, Integration of vSphere Storage for Kubernetes, Dynamic storage provisioning of PVC.
Step3: Configure custom Docker image on the Docker hub containing MongoDB, ycsb & the relevant packages to run ycsb workloads.
Step4: Load testing MongoDB using ycsb and obtaining the test results.
Step1: Installing Kubernetes cluster on ESXi VMs
Environment used:
vSphere 6.7 Update 3 infrastructure.
VM folder in vSphere to collect the kubernetes VMs.
ESXi hosts – version 6.7 u3.
Guest OS – CentOS Linux release 7.8.2003 (Core).
Cluster with HA & DRS enabled.
The following steps will run on the Master-Node.
Prepare Hostname, SELinux and Firewall
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname VM1-master
[root@vm1-master ~]# setenforce 0
[root@vm1-master ~]# sed -i --follow-symlinks 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
[root@vm1-master ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=6443/tcp
[root@vm1-master ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2379-2380/tcp
[root@vm1-master ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10250/tcp
[root@vm1-master ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10251/tcp
[root@vm1-master ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10252/tcp
[root@vm1-master ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10255/tcp
[root@vm1-master ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
[root@vm1-master ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@vm1-master ~]# echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
[root@vm1-master ~]# cat /etc/hosts
10.20.176.108 VM1-master
10.20.176.110 VM2-worker
10.20.176.111 VM3-worker
Setup K8s repository
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install Docker, Kubeadm
[root@vm1-master ~]# yum install kubeadm docker -y
[root@vm1-master ~]# systemctl restart docker && systemctl enable docker
[root@vm1-master ~]# systemctl restart kubelet && systemctl enable kubelet
[root@vm1-master ~]# swapoff -a
Initialize kubernetes cluster
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubeadm init
.
.
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 10.20.176.108:6443 --token 12a5v2.fwneclcqgri0whof \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:fdb98ddc292f0329cf19784e75cd359f07f560ef9aa8379f042fded7be517c7e
To use a sudo enabled user, run:
[root@vm1-master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
[root@vm1-master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
[root@vm1-master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Deploy POD Network
[root@vm1-master ~]# export kubever=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$kubever"
Check to see if the kubectl command is activated.
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
vm1-master Ready master 31m v1.19.2
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-f9fd979d6-2qmqt 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system coredns-f9fd979d6-knl57 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system etcd-vm1-master 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system kube-apiserver-vm1-master 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-vm1-master 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system kube-proxy-gjqhw 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system kube-scheduler-vm1-master 1/1 Running 0 31m
kube-system weave-net-lnhps 2/2 Running 0 27m
The following steps will run on both the Worker-Nodes.
Prepare Hostname, SELinux and Firewall
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname VM2-worker
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# sed -i --follow-symlinks 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=6783/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10250/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10255/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30000-32767/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@localhost ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@localhost ~]# echo '1' > /proc/sys/net/bridge/bridge-nf-call-iptables
[root@vm2-worker ~]# cat /etc/hosts
10.20.176.108 VM1-master
10.20.176.110 VM2-worker
10.20.176.111 VM3-worker
Setup K8s repository
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install Docker, Kubeadm
[root@localhost ~]# yum install kubeadm docker -y
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart docker && systemctl enable docker
[root@localhost ~]# swapoff -a
Join the Worker Node to the Kubernetes Cluster
(To be obtained from above master-node kubeadm init results)
[root@localhost ~]# kubeadm join 10.20.176.108:6443 --token 12a5v2.fwneclcqgri0whof --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:fdb98ddc292f0329cf19784e75cd359f07f560ef9aa8379f042fded7be517c7e
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
Note: As suggested go back to your master-node and check if worker-node have joined the cluster using the following command.
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
vm1-master Ready master 3h23m v1.19.2
vm2-worker Ready <none> 144m v1.19.2
vm3-worker Ready <none> 131m v1.19.2
Step2: Configure vSphere cloud provider, Integration of vSphere Storage for Kubernetes, Dynamic storage provisioning of PVC
Prerequisites:
- All Kubernetes VMs must be placed in a vSphere VM folder.
- The disk.EnableUUID parameter must be set to TRUE for Kubernetes Node VMs.
- Configure Storage Policy-Based Management (SPBM) with VMFS - https://support.purestorage.com/Solutions/VMware_Platform_Guide/User_Guides_for_VMware_Solutions/VMware_Cloud_Native_Storage_User_Guide/Using_Storage_Policy_Based_Management_(SPBM)_with_VMFS
- Use above SPBM VMFS as default-datastore in the below configuration.
- Install jq, govc on master-node.
# Configuring the Kubernetes vSphere Cloud Provider On the Kubernetes Master node, Create vsphere.conf Create the vSphere configuration file in /etc/kubernetes/vcp/vsphere.conf - you’ll need to create the folder. [root@vm1-master ~]# cat /etc/kubernetes/vcp/vsphere.conf [Global] user = "[email protected]" password = "Passw0rd" port = "443" insecure-flag = "1" [VirtualCenter "10.20.176.180"] datacenters = "munavar" [Workspace] server = "10.20.176.180" datacenter = "munavar" default-datastore = "wsame_large" resourcepool-path = "munavar/Resources" folder = "TKG" [Disk] scsicontrollertype = pvscsi Modify the kubelet service Append the --cloud-provider and --cloud-config flags to /var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env [root@vm1-master ~]# cat /var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env KUBELET_KUBEADM_ARGS="--network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2 --cloud-provider=vsphere --cloud-config=/etc/kubernetes/vcp/vsphere.conf" Modify container manifests The container manifests for the Kubernetes API server and controller-manager also need to be updated with the --cloud-provider and --cloud-config flags. These are located in the /etc/kubernetes/manifests folder. Add the following to the spec:containers:command array, paying attention to whitespace (it is yaml, after all!) - --cloud-provider=vsphere - --cloud-config=/etc/kubernetes/vcp/vsphere.conf We also need add a mount for the vsphere.conf file location in spec:containers:volumeMounts - mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/vcp name: vcp readOnly: true And a volume in spec:volumes - hostPath: path: /etc/kubernetes/vcp type: DirectoryOrCreate name: vcp On the Kubernetes Worker nodes Modify the kubelet service Append only the --cloud-provider flag to /var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env [root@vm2-worker ~]# cat /var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env KUBELET_KUBEADM_ARGS="--network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2 --cloud-provider=vsphere" [root@vm3-worker ~]# cat /var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env KUBELET_KUBEADM_ARGS="--network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2 --cloud-provider=vsphere Update the Node Provide IDs - from Master node [root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl get nodes -o json | jq '.items[]|[.metadata.name, .spec.providerID, .status.nodeInfo.systemUUID]' [ "vm1-master", null, "4B531942-57E8-4A59-CFC8-72556461DAC7" ] [ "vm2-worker", null, "844C1942-185E-DD1A-AD54-843BEC5F6EF8" ] [ "vm3-worker", null, "CB251942-8386-DC5F-0863-2F5921D09456" ] If the output contains 'null' for the providerId, then you need to set it: the documentation provides a script - please refer to it https://vmware.github.io/vsphere-storage-for-kubernetes/documentation/existing.html#update-all-node-providerid-fields Once the script is run, we may get the following output [root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl get nodes -o json | jq '.items[]|[.metadata.name, .spec.providerID, .status.nodeInfo.systemUUID]' [ "vm1-master", "vsphere://4219534B-E857-594A-CFC8-72556461DAC7", "4B531942-57E8-4A59-CFC8-72556461DAC7" ] [ "vm2-worker", "vsphere://42194C84-5E18-1ADD-AD54-843BEC5F6EF8", "844C1942-185E-DD1A-AD54-843BEC5F6EF8" ] [ "vm3-worker", "vsphere://421925CB-8683-5FDC-0863-2F5921D09456", "CB251942-8386-DC5F-0863-2F5921D09456" ] Consuming vSphere Storage - Create Storage Class Note: Storage policies should be created on vSphere using SPBM VMFS before creating below storage class [root@vm1-master ~]# cat sc-vsan-policy.yaml kind: StorageClass apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: fast provisioner: kubernetes.io/vsphere-volume parameters: diskformat: thin storagePolicyName: kubernetes datastore: wsame_large [root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl create -f sc-vsan-policy.yaml storageclass.storage.k8s.io/fast created [root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl describe storageclass Name: fast IsDefaultClass: No Annotations: <none> Provisioner: kubernetes.io/vsphere-volume Parameters: datastore=wsame_large,diskformat=thin,storagePolicyName=kubernetes AllowVolumeExpansion: <unset> MountOptions: <none> ReclaimPolicy: Delete VolumeBindingMode: Immediate Events: <none> Create a Persistent Volume Claim - Dynamic volume provisioning [root@vm1-master ~]# cat vsphere-volume-pvcsc.yaml kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: pvc-volume1 annotations: volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: fast spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 250Gi [root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl create -f vsphere-volume-pvcsc.yaml persistentvolumeclaim/pvc-volume1 created [root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl describe pvc pvc-volume1 Name: pvc-volume1 Namespace: default StorageClass: fast Status: Bound Volume: pvc-7b58289a-709d-46f5-9e6c-585aba78f7d5 Labels: <none> Annotations: pv.kubernetes.io/bind-completed: yes pv.kubernetes.io/bound-by-controller: yes volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: fast volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-provisioner: kubernetes.io/vsphere-volume Finalizers: [kubernetes.io/pvc-protection] Capacity: 250Gi Access Modes: RWO VolumeMode: Filesystem Mounted By: <none> Events: <none> [root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl describe pv Name: pvc-7b58289a-709d-46f5-9e6c-585aba78f7d5 Labels: <none> Annotations: kubernetes.io/createdby: vsphere-volume-dynamic-provisioner pv.kubernetes.io/bound-by-controller: yes pv.kubernetes.io/provisioned-by: kubernetes.io/vsphere-volume Finalizers: [kubernetes.io/pv-protection] StorageClass: fast Status: Bound Claim: default/pvc-volume1 Reclaim Policy: Delete Access Modes: RWO VolumeMode: Filesystem Capacity: 250Gi Node Affinity: <none> Message: Source: Type: vSphereVolume (a Persistent Disk resource in vSphere) VolumePath: [wsame_large] kubevols/kubernetes-dynamic-pvc-7b58289a-709d-46f5-9e6c-585aba78f7d5.vmdk FSType: ext4 StoragePolicyName: kubernetes Events: <none>
Step3: Configure custom Docker image on the Docker hub containing MongoDB, ycsb, Python, maven & java to run ycsb workloads installed as part of Docker image
- Create public docker hub where we can push the custom docker image inorder to use.
- docker login –username= <Repository name>
- docker build -t <Image Name> . ==>This Dot indicates the location where Dockerfile is placed.
- docker tag <image name:tag> <repository name/image name :tag>
Once the Custom docker image is pushed into Docker hub, we can pull the image using
docker pull <repository name/image name :tag> for later usage.
MongoDB on Kubernetes with StatefulSets
[root@vm1-master ~]# cat mongo.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: mongodb-replica
spec:
serviceName: database
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: database
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: database
selector: mongodb-replica
spec:
containers:
- name: mongodb-stand
image: arundockerregistry/mymongo:v2
ports:
- containerPort: 27017
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: mongo-persistent-storage
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: "fast"
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 500Gi
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl create -f mongo.yaml
statefulset.apps/mongodb-replica created
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mongodb-replica-0 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
mongodb-replica-1 1/1 Running 0 6m19s
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
mongo-persistent-storage-mongodb-replica-0 Bound pvc-f974bbbc-266c-4789-ad25-8e6493f38eea 500Gi RWO fast 6m41s
mongo-persistent-storage-mongodb-replica-1 Bound pvc-4bc36d34-27a7-4dcb-b36d-b503364b22a2 500Gi RWO fast 6m37s
[root@vm1-master ~]# kubectl exec -i -t mongodb-replica-0 -- bash
root@mongodb-replica-0:/# ls
bin data docker-entrypoint-initdb.d home lib media opt root sbin sys usr ycsb-0.5.0 boot dev etc js-yaml.js lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var ycsb-0.5.0.tar.gz
root@mongodb-replica-0:/# java -version
openjdk version "1.8.0_265"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_265-8u265-b01-0ubuntu2~16.04-b01)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.265-b01, mixed mode)
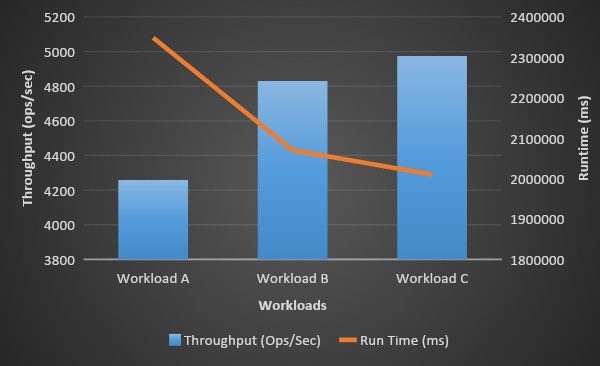
Step4: Load testing MongoDB using YCSB and obtaining the test results.
YCSB is a popular Java open-source specification and program suite developed at Yahoo! to compare the relative performance of various NoSQL databases. Its workloads are used in various comparative studies of NoSQL databases
Workloads Used:
we chosen workloads A, B, C.
Workload A: Update heavy workload: 50/50% Mix of Reads/Writes
Workload B: Read mostly workload: 95/5% Mix of Reads/Writes
Workload C: Read-only: 100% reads.
The following command was used to run workload A,B & C on MongoDB pod:
/root/ycsb-0.5.0/bin/ycsb load mongodb -s -P /root/ycsb-0.5.0/workloads/workloada -p recordcount=10000000 /root/ycsb-0.5.0/bin/ycsb run mongodb -s -P /root/ycsb-0.5.0/workloads/workloada -p operationcount=10000000 /root/ycsb-0.5.0/bin/ycsb load mongodb -s -P /root/ycsb-0.5.0/workloads/workloadb -p recordcount=10000000 /root/ycsb-0.5.0/bin/ycsb run mongodb -s -P /root/ycsb-0.5.0/workloads/workloadb -p operationcount=10000000 /root/ycsb-0.5.0/bin/ycsb load mongodb -s -P /root/ycsb-0.5.0/workloads/workloadc -p recordcount=10000000 /root/ycsb-0.5.0/bin/ycsb run mongodb -s -P /root/ycsb-0.5.0/workloads/workloadc -p operationcount=10000000
Challenges Faced:
- Faced an issue during dynamic volume provisioning (PVC creation) fails with message - No VM found.
- Resolved it by following this comment - create Kubernetes master with vsphere cloud provider and add worker nodes after that with vsphere cloud provider.
https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/71502
References:
- https://www.linuxtechi.com/install-kubernetes-1-7-centos7-rhel7/
- https://support.purestorage.com/Solutions/VMware_Platform_Guide/User_Guides_for_VMware_Solutions/VMware_Cloud_Native_Storage_User_Guide/Using_Storage_Policy_Based_Management_(SPBM)_with_VMFS
- https://www.definit.co.uk/2019/06/lab-guide-kubernetes-and-storage-with-the-vsphere-cloud-provider-step-by-step/
- https://vmware.github.io/vsphere-storage-for-kubernetes/documentation/existing.html#update-all-node-providerid-fields
- https://github.com/brianfrankcooper/YCSB/wiki/Running-a-Workload
