What is the Importance of NVMe and NVMe-oF in Modern Storage?

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
What is NVMe?
NVMe is the new protocol which is known as Non Volatile Memory Express. Let’s have a brief idea about volatile and non-volatile memory before moving ahead to the details of the topic. Volatile memory is a type of memory where the data is lost, in-case of power failure. RAM is a good example of volatile memory. In contrast to volatile memory, non-volatile memory is the type of memory which will retain the data in case of a power failure as there is a battery providing the back-up. Flash is non-volatile memory and of two types- nand and nor flash memory.
NVM Express (NVMe)
NVM Express® (NVMe™) is an optimized, high-performance scalable host controller interface designed to address the needs of Enterprise and Client systems that utilize PCI Express®-based solid-state storage. (https://nvmexpress.org/wp-content/uploads/NVMe_Overview.pdf). Solid-state drives (SSD) are nothing but storage made by two key components- viz. nand flash chips and flash controller. SSDs are faster than traditional hard drives as these drives have no spinning component.
Need for PCIE based NVMe SSDs
All hot data should be available on flash. Now-a-days data is like gold mine, faster processing of data can have a great impact on business decisions. For achieving this kind of speed, flash based storage devices and high speed storage protocol like NVMe is required. NVMe has made its mark as a high-performance protocol and is expanding due to an industry wide adoption by storage vendors. PCIe based NVMe SSD drives achieve that speed because NVMe supports 64k commands per queue and 64 queues whereas the SATA devices support 32 and SaaS devices support up to 256 commands per queue. Hence concluding that NVMe leverages all the potential of flash-based SSDs. This technology has emerged for reducing the gap between fast CPU and slow storage. Datacenter, Gaming and entertainment industries will have great performance benefits through NVMe. Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIE) are also evolving in order to support NVMe.
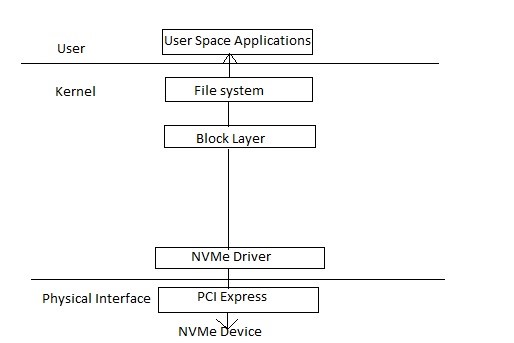
Diagram of PCIE NVMe storage IO stack[/capntion]
DMA and RDMA
A. DMA
Direct Memory Access provides faster data transfer rate by reducing the CPU cycle of fetching, decoding, and executing the IO. It enables faster processing as the CPU can be utilized in other operations while data transfer is going on. You need a DMA controller for carrying out the operation.
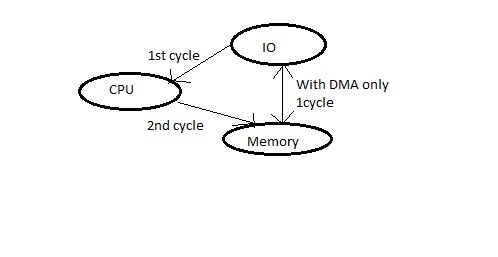 Above is the simple example of CPU cycle
Above is the simple example of CPU cycle
B. RDMA
Let’s try to split the term and understand what Remote Direct Memory Access widely means. It is a direct memory access to a remote host’s DMA from a separate computer’s memory without involving the operating system. This increases the throughput low latency networking as this uses zero-copy, which implies that the data transfer is done without the networking stack, data is received or sent directly to the buffers, without being copied between the network stack. In addition, the RDMA bypasses the kernel, data that is transferred from user space. It is used in many markets; some of them are-
HPC – High performance computing, BIG data, cloud, FSI (Finance services and insurance). For using RDMA, one needs a network adapter that supports RDMA. It should supports Ethernet or Infiniband as link layer protocol.
NVMe over fabrics (NVMe-oF)
NVMe over fabrics is a technology, which enables the extension of distance by which PCIE NVMe based hosts and storage drivers can be connected. NVMe-oF standard supports multiple storage networking fabrics for example Ethernet, Infiniband and FC.
For Ethernet, RoCE v2 and iWARP are ideal RDMA fabrics. Mellanox is the leading manufacturer of RoCE based network adapter where as Qlogic has FC-NVMe ready adapters. The desired difference in latency is 10 microseconds between a distant NVMe device and a device sitting locally. The NVMe-oF solution provides the NVMe storage on a high-speed storage network to multiple hosts increasing the throughput and with low latency. Most of the areas in NVMe over fabrics are the same as the local NVMe protocol- for instance I/O and administrative commands, NVMe namespaces, registers and properties, power states, reservations, etc.
There are some differences in identifier, discovery, queuing and data transfers. Disaggregation of storage from compute, higher utilization of SSDs and leveraging the CPU to its fullest capacity other than transferring the data only, are key benefits for a cloud infrastructure. NVMe over fabric works on a message based system where the NVMe commands or responses are encapsulated into capsules.
Conclusion
The NVMe PCIe SSDs and over fabrics will drive future storage industry and it will add value to the business by helping the cloud infrastructure and big data analytics achieve fast access to Data.
Lead storage vendors have shown their interest in these areas and some of them have already shipped their products with this specification and some of them are in-design phase of their products.
