What’s new in NFS v4.2?

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
NFS v4.2: new features and beyond!
There is much interest amongst storage professionals to learn about new features of NFS v4.2 and understand how these features help to meet the current requirements of the storage industry.
NFS v4.2 has solved a number of performance issues and brings enhancement for NFS v4.1 with its new features. These new features aim to provide features of the common local file system that were not available in earlier versions of NFS and to offer these features remotely.
Discussed below are details of the new features introduced in NFS v4.2:
1. Server Side Clone Copy:
There was network overhead problem associated with the traditional file copy of remotely accessed file, whether done from one server to another server or between locations in the same server as the data was sent twice on the network. (Source to client then client to destination).
New operations introduced in NFS v4.2 remove network overhead by:
- Intra-Server Clone: It allows the client to request synchronous cloning.
- Intra-Server Copy: It allows the client to request the server to perform copy internally.
- Inter-Server Copy: It allows the client to authorize source and destination servers to interact directly.
2. Application Input / Output Advice:
- Clients and applications advise the server about expected I/O behavior.
- It helps to optimize I/O request from the file by prefetching or evicting data (caching).
- Following is the I/O behavior communicated by clients and application to server:
- File Access Pattern: Whether Sequential or Random
- File Access in Near Future: Whether file would be accessed in near future or not
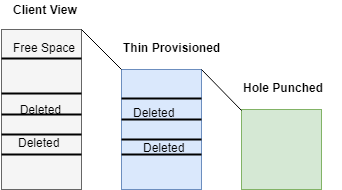
3. Sparse Files:
Sparse files are defined as those files that have unallocated data or uninitialized data blocks as holes in the file. These are transferred as zeros when read from the file.
- READ_PLUS: Server sends to client metadata which describes holes.
- DEALLOCATE: It allows the client to punch holes in the file.
- SEEK: Provides scan for next hole.
4. Space Reservations:
- It ensures that files have space reservation.
- For sparse files the application needs to ensure that there needs to be always data blocks for future writes.
- ALLOCATE: Allows the client to request for the guarantee that space would be available.
- DEALLOCATE: Allows the client to punch holes into files and release space reservation.
5. Application Data Block (ADB) Support:
There are some applications which treat a file like a disk and want to format the file image.
-
- WRITE_SAME: Sends metadata on the server to allow it to write block contents.
6. Labeled NFS:
- Both the client and server use MAC ( Mandatory Access Control) security models to enforce data access.
- For labeled New file object an attribute called sec_label is introduced.
- sec_label: It allows the server to string the MAC labels on file, which the client can retrieve and restore for data access.
7. Layout Enhancements:
- It allows the client to communicate back to metadata server with following details.
-
- Error details
- Performance characteristics with storage devices
- It was not possible for NFS v4.1 clients to communicate back to metadata server with these details.
- Two new operations are introduced for the client to communicate with metadata server:
- LAYOUTERROR: Client can use LAYOUTERROR to inform metadata server about any errors in interaction with layouts which could be represented by the current file handle, client ID details, byte range information and lea_stateid
- LAYOUTSTATS: It is used to inform metadata server about interaction with layout represented by current file_handle, client ID, byte range and lsa_stateid.
