Object Based vs Image Based Identification: An overview

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
Crucial factors in choosing mobile testing tools
The object identification technique that is used in the different automation tools offering mobile application testing has proven to be quite a crucial factor in identifying the lucrative choice from amongst the many tools available in the market. Most major tools are based on scripts that are designed to identify objects in the AUT using either the image based identification or native identification technique. While certain tools work using both the aforementioned techniques of object identification concerns of robustness and execution time makes tools based on a single technique of object identification the preferred choice amongst the QA personnel. Upon having ensured that the overall features of the mobile test automation tools are in keeping with the market standards, the final choice tends to be greatly affected by the object identification technique that they utilize.
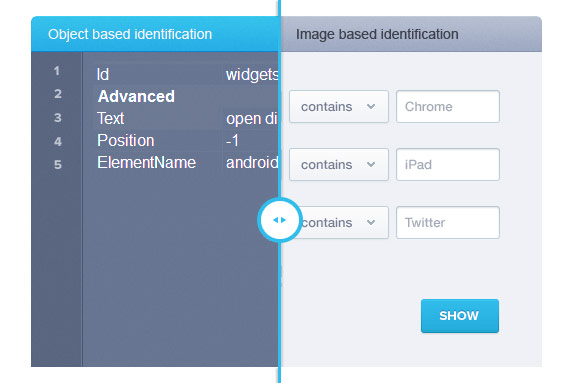
The image based identification technique
This technique of object identification is based on the GUI overlay that the application features. This has made the tools featuring this technique the preferred option in instances where the testing processes are required to cover multiple platforms and operating systems. In utilizing the GUI for the identification process, this technique is based on the image processing attributes of the objects in the AUT. Besides, the identification process, in being carried out by means of optical character recognition has ensured that in instances where third party application access is required is compatible with tools that utilize this technique.
The drawbacks
The optical character recognition, despite its tendency to increase performance metrics of the device, has proven to be a defining feature in the IBT technique. However, one of the biggest drawbacks in the IBT is its tendency to crash in instances where the process involves dynamic changes in the application. Moreover, tools using IBT for the object identification process tend to take a considerably longer execution time when compared to those using the native identification techniques, owing to its need to process images and to ensure that it remains the same in each instance of recording. Besides, testers not being able to identify the individual steps that are involved in the many complex actions being performed by the Application under Test (AUT) has proven to be a major drawback in this technique.
The native identification technique
This technique of object identification is based on recognizing the nativity of the objects in the AUT. This nativity recognition process for each individual object in the application is carried out using different attributes that are assigned to the object. This ensures that in cases where one attribute is absent, the other, or a combination of the available attributes is utilized for the recognition process. Some of the attributes that are commonly taken into consideration, for the process of nativity recognition includes the ID, the text or the position assigned to the object. Tools like MTAS, in utilizing the native identification technique and gathering the attributes of the objects in the AUT, have proven to be quite effective in terms of the test execution time involved. Besides, such tools have proven to be quite reliable in instances of an object missing specific data, where the tool is able to recognize the available data and execute the task without any hassles.
The drawbacks
The recognition of the individual attributes of the objects involved restricts this technique’s ability to function in test scenarios that require third party application access, which happens to reduce the automation coverage capability of the tools utilizing this technique.
Factors to consider in making the choice
In choosing the tools based on their object identification technique, the QA personnel involved ought to ensure that the tools offer the lowest possible test execution time, and a hassle free test experience, both factors that are crucial in ensuring minimal time to market for the applications being developed.
