Navigating the Transition: On Premise to Cloud Migration Explained

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses constantly seek ways to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and improve overall efficiency. One significant shift many enterprises are undertaking is migrating from traditional on-premise infrastructure to cloud-based solutions. This transition, known as “on premise to cloud migration,” holds immense potential for organizations across various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of this transition, exploring its benefits, challenges, best practices, and key considerations.
Understanding On Premise to Cloud Migration
In IT infrastructure, “on premises physical infrastructure” refers to physical servers, storage devices, and networking equipment housed within an organization’s premises or data centers. Internal IT teams meticulously manage these on-premise resources, ensuring data security, availability, and performance. However, the inherent limitations of on premises infrastructure, including finite capacity, scalability challenges, and high maintenance costs, have spurred the adoption of cloud computing as a compelling alternative.
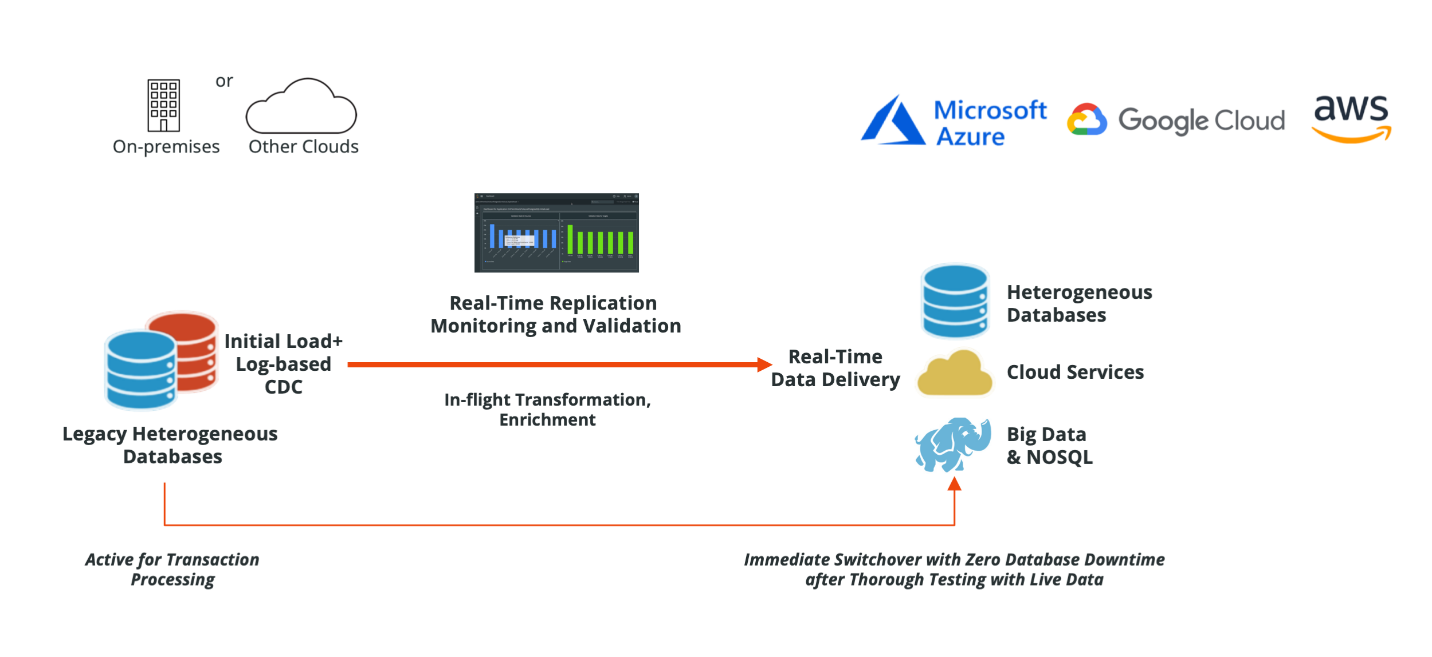
Source: Striim
Cloud migration involves the meticulous planning, execution, and optimization of the transition process, aiming to harness the full potential of cloud technologies while minimizing disruption to business operations. This endeavor encompasses various facets, each demanding careful planning, consideration, and technical expertise:
Data Migration Strategies
Data migration is a critical aspect of on premise to cloud migration. It involves transferring vast volumes of data from local storage systems to remote cloud repositories. This process consists in selecting appropriate migration methods, such as bulk transfers, incremental synchronization, or real-time replication transfer data over, depending on data volume, latency requirements, and downtime tolerance.
Source: Spiceworks
Application Re-Platforming and Re-Architecting
On premise to cloud migration necessitates architectural adjustments and optimization to align with the characteristics and capabilities of cloud platforms. This may involve re-platforming existing applications to leverage cloud-native services and frameworks, such as serverless computing, containerization, or microservices architecture. Alternatively, complex legacy applications may require re-architecting efforts to modularize components, decouple dependencies, and enhance scalability and resilience.
Network Configuration and Connectivity
Seamless integration between on premises data center infrastructure and cloud environments requires meticulous network configuration and connectivity planning. This entails establishing secure communication channels, such as virtual private networks (VPNs) or dedicated leased lines, to facilitate data transfer, application access, and interconnectivity between on-premise data centers and cloud regions. Additionally, organizations must implement robust network security measures, including firewall policies, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and encryption protocols, to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality across hybrid environments.
Performance Optimization and Monitoring
Ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization in the cloud necessitates continuous monitoring and optimization of workloads, infrastructure components, and application dependencies. Cloud-native monitoring tools and performance metrics provide granular insights into resource utilization, latency, throughput, and error rates, enabling IT teams to identify bottlenecks, fine-tune configurations, and optimize resource allocation for optimal efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Protecting sensitive data and ensuring regulatory compliance are paramount concerns in on premise to cloud migration. Cloud service provider offer many security features, including data encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and compliance certifications (e.g., SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA), to fortify cloud environments against cyber threats and regulatory violations. However, organizations must implement robust security controls, data encryption protocols, and access management policies to mitigate risks and maintain compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Capacity Planning and Cost Optimization
Effective capacity planning and cost optimization are essential components of a cloud migration strategy, aiming to balance resource availability, performance requirements, and budget constraints. Cloud providers offer flexible pricing models, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot instances, enabling organizations to optimize costs based on workload characteristics, usage patterns, and budgetary considerations. Additionally, the cloud provider’ cost management tools and services facilitate cost tracking, budget forecasting, and cost optimization recommendations, empowering organizations to maximize ROI and minimize expenditure in the cloud.
The Benefits of Cloud Migration
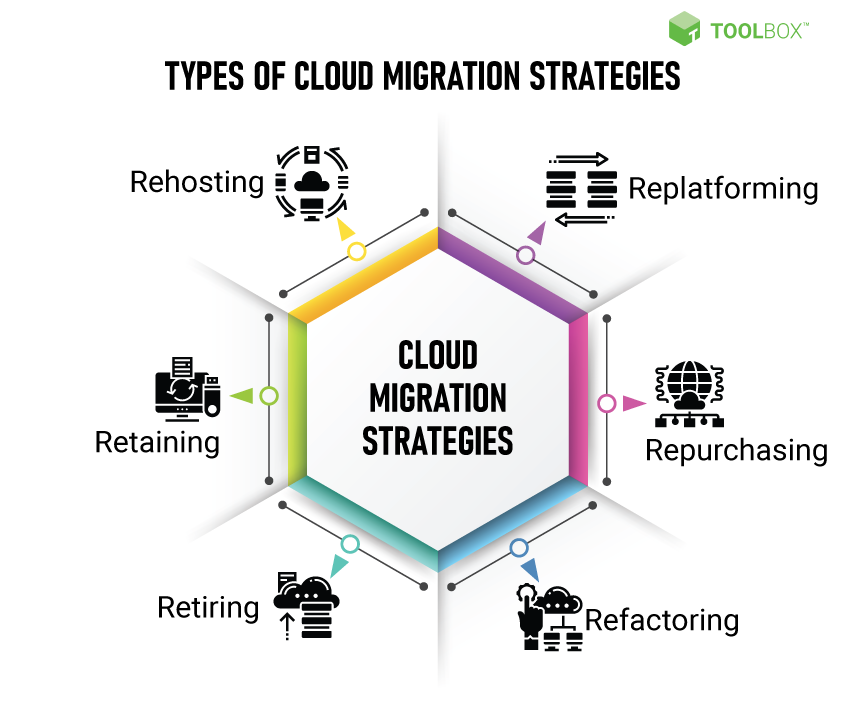
Source: Data Dynamics
Scalability and Flexibility: The Elasticity Advantage
Cloud-based solutions boast an inherent elasticity that dynamically empowers organizations to scale resources in response to fluctuating workloads and demands. Leveraging auto-scaling capabilities and resource provisioning mechanisms, such as Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling or Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler, enables businesses to seamlessly adjust compute, storage, and networking resources in real time, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency. This elasticity ensures that applications can gracefully handle sudden spikes in traffic or processing requirements without compromising performance or availability. This enables organizations to deliver superior user experiences and maintain competitive agility in dynamic market environments.
Cost Savings: Capitalizing on Cloud Economics
Cloud migration represents a paradigm shift in IT economics. It offers compelling cost-saving opportunities by eliminating capital expenditures (CapEx) associated with hardware procurement, maintenance, and infrastructure depreciation. Organizations can realize significant cost efficiencies and resource optimization benefits by transitioning to a subscription-based operational expenditure (OpEx) model.
Cloud providers, such as Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offer flexible pricing models, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot instances. These enable organizations to align costs with actual usage and scale resources based on evolving business requirements. Furthermore, cloud cost management tools, such as AWS Cost Explorer and Azure Cost Management, empower organizations to track, analyze, and optimize cloud spending, maximizing ROI and minimizing unnecessary expenditures.
Enhanced Collaboration: Breaking Down Geographical Barriers
Cloud platforms catalyze collaboration, breaking geographical barriers and fostering seamless communication and teamwork among distributed teams and stakeholders. Organizations can use cloud-based collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Google Workspace to facilitate real-time communication, document sharing, and project collaboration across disparate locations and time zones.
Cloud-based project management and productivity suites, such as Asana, Trello, and Jira Cloud, streamline task management, workflow orchestration, and team coordination, promoting greater productivity, innovation, and synergy within cross-functional teams. This democratization of collaboration transcends traditional organizational boundaries, enabling remote and distributed teams to collaborate effectively and drive collective success in an increasingly interconnected and decentralized digital landscape.
Improved Security: Fortifying Cyber Defense Posture
Cloud migration allows organizations to enhance their cyber defense posture by leveraging the advanced security features and compliance frameworks cloud service providers provide. Cloud platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and GCP, adhere to stringent security standards, including ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR, to safeguard customer data and mitigate cybersecurity risks. Implementing robust identity and access management (IAM) controls, encryption protocols, and network security policies ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability across cloud environments.
Furthermore, cloud-native security solutions, such as AWS Security Hub, Azure Security Center, and Google Cloud Security Command Center, offer centralized threat detection, vulnerability management, and compliance monitoring capabilities, enabling organizations to identify and mitigate security threats and compliance gaps proactively. By embracing a holistic approach to cloud security, organizations can instill confidence in their stakeholders, protect sensitive assets, and uphold regulatory compliance obligations in an increasingly hostile cyber landscape.
Business Continuity: Safeguarding Against Disruption
Cloud-based disaster recovery (DR) and backup solutions provide organizations with resilient and scalable mechanisms to ensure data redundancy, continuity of operations, and rapid recovery in the event of a disaster or service outage. Leveraging cloud-native DRaaS (Disaster Recovery as a Service) offerings, such as AWS Disaster Recovery, Azure Site Recovery, and GCP Disaster Recovery, organizations can replicate mission-critical workloads, applications, and data to geographically dispersed cloud regions, minimizing single points of failure and enhancing resilience against natural disasters, hardware failures, or human errors.
Cloud-based backup and archival solutions, such as AWS, Azure, and GCP Storage, enable organizations to securely store and retrieve data across multiple storage tiers, ensuring data durability, integrity, and accessibility over extended retention periods. By embracing cloud-based business continuity strategies, organizations can mitigate operational risks, minimize downtime, and maintain business continuity in the face of unforeseen disruptions, safeguarding their reputation, revenue, and competitive advantage in an increasingly volatile and unpredictable business landscape.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of cloud migration are undeniable, the transition process to other cloud providers comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
Data Security and Compliance: Safeguarding the Crown Jewels
As organizations embark on the difficult journey of data migration to the cloud, ensuring the sanctity of sensitive data and compliance with regulatory mandates becomes paramount. By implementing robust encryption protocols, data masking techniques, and access control mechanisms on premises data, organizations can fortify their data fortresses against cyber marauders and nefarious actors.
Furthermore, leveraging cloud-native security features, such as AWS Key Management Service (KMS), Azure Information Protection, and Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM), enables organizations to erect impenetrable barriers around their digital citadels, safeguarding sensitive assets from prying eyes and regulatory scrutiny. By wielding the sword of compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, organizations can defeat the specter of legal liabilities and preserve the honor of their data kingdom.
Integration Complexity: Untangling the Web of Interdependencies
The labyrinthine path of integrating legacy on-premise systems with cloud-based solutions poses a Herculean challenge for organizations venturing into digital transformation. Navigating through a maze of APIs, data connectors, and middleware, organizations must orchestrate a symphony of data flows and transactional interactions between disparate systems and platforms. Embracing modern integration paradigms, such as microservices architecture, event-driven architecture, and API gateways, organizations can unravel the Gordian knot of integration complexity, fostering seamless interoperability and data exchange across hybrid environments.
By harnessing the power of cloud integration and platforms, such as MuleSoft Anypoint Platform, Azure Integration Services, and Google Cloud Pub/Sub, organizations can transcend the boundaries of legacy silos and forge a unified ecosystem of interconnected applications, services, and data sources, laying the foundation for innovation and agility in the digital age.
Legacy Applications: Breathing New Life into Relics of the Past
As organizations embark on the odyssey of cloud migration, they must confront the formidable challenge of modernizing legacy applications in the cobwebs of obsolescence and inefficiency. Armed with the sword of refactoring, organizations can wield the transformative power of cloud-native architectures, such as containers, serverless computing, and Kubernetes orchestration, to breathe new life into archaic monoliths and legacy codebases. By decoupling dependencies, modularizing components, and embracing cloud-native design patterns, organizations can liberate their applications from the shackles of antiquity, enabling them to soar to new heights of scalability, resilience, and agility in the cloud.
Alternatively, organizations may embark on the dangerous quest of application replacement for artifacts beyond redemption, seeking refuge in embracing modern SaaS offerings or bespoke cloud-native solutions tailored to their unique needs. Thus, by embracing the spirit of innovation and adaptation, organizations can transcend the limitations of legacy baggage and embark on a transformative journey toward digital excellence and competitive advantage in the cloud era.
Performance and Latency: Racing Against the Clock
Organizations must navigate treacherous waters fraught with perilous currents of performance bottlenecks and latency labyrinths as they set sail on the turbulent seas of cloud migration. Depending on the nature of workloads and network configurations, organizations may encounter tempestuous storms of latency, packet loss, and jitter, threatening to capsize their digital vessels and plunge them into the abyss of operational chaos. By leveraging cloud-native optimization techniques, such as content delivery networks (CDNs), edge computing, and data caching, organizations can harness the winds of performance optimization to propel their workloads to new heights of speed and efficiency.
Embracing hybrid cloud architectures and multi-cloud strategies enables organizations to strategically distribute workloads across geographically dispersed data centers and cloud regions, minimizing latency and maximizing throughput. Thus, by mastering the art of performance tuning and latency mitigation, organizations can chart a course toward smoother sailing and swifter navigation in the vast expanse of the next cloud environment.
Change Management: Leading the Charge of Digital Revolution
As organizations embark on the epic quest of cloud migration, they must rally their forces and lead the charge of digital revolution against the citadel of status quo and inertia. Armed with the banners of cultural transformation, skill empowerment, and organizational agility, organizations can defeat the specter of resistance following cloud migration challenges and shepherd their people through the crucible of change. By fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning, organizations can nurture a cadre of digital warriors equipped with the knowledge, skills, and mindset to embrace cloud migration challenges and drive organizational success in the digital age.
Through effective communication, stakeholder engagement, and training initiatives, organizations can cultivate a sense of ownership and empowerment among their workforce, inspiring them to embrace change as a catalyst for growth and transformation. Thus, by leading the charge of change management with courage and conviction, organizations can embark on a transformative journey toward digital excellence and resilience in the cloud-powered future.
Best Practices for Successful Migration
To mitigate risks and maximize the benefits of on-premise to cloud migration, organizations should adhere to best practices:
Thorough Planning: Blueprinting the Cloud Odyssey
Embark on the quest of cloud migration by meticulously mapping out the terrain of your existing infrastructure, workloads, and interdependencies. Conduct a comprehensive assessment encompassing network topology, application architecture, data dependencies, and regulatory compliance requirements to chart a course toward cloud nirvana. By developing a detailed cloud migration plan now, organizations can confidently navigate the treacherous waters of migration, anticipating challenges, and orchestrating a seamless transition to the promised land of cloud excellence.
Prioritize Workloads: Deciphering the Cloud Hieroglyphics
Unravel the enigma of workload prioritization by deciphering the cryptic glyphs of criticality, complexity, and compatibility. Prioritize workloads based on their strategic importance, technical intricacy, and suitability for cloud environments, ensuring strategic alignment with organizational objectives and resource constraints. Organizations can allocate resources judiciously and expedite the migration journey with purpose and precision by discerning between mission-critical juggernauts and inconsequential ephemera.
Data Migration Strategies: Unveiling the Migration Alchemy
Embark on a voyage of data migration alchemy, where bytes transform into gold through the arcane arts of lift-and-shift, re-platforming, and re-architecting. Choose the optimal data migration project strategy tailored to the unique characteristics of your data estate, balancing factors such as volume, velocity, and variability. Whether traversing the path of minimal disruption with lift-and-shift, optimizing for cloud-native paradigms with re-platforming, or embarking on a quest for digital transformation through re-architecting, organizations can unlock the transformative potential of data migration and pave the way for future innovation and agility in the cloud.
Security and Compliance: Fortifying the Cloud Bastion
Erect an impregnable fortress of security and compliance to safeguard your digital dominion from the marauding hordes of cyber adversaries and regulatory watchdogs. Implement a multi-layered defense strategy encompassing robust encryption protocols, identity and access management (IAM) controls, and compliance frameworks to fortify data sovereignty and uphold regulatory mandates. By wielding the sword of compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, organizations can repel the forces of chaos and preserve the sanctity of their digital realm in the cloud.
Performance Monitoring: Navigating the Cloud Cartography
Navigate the labyrinthine expanse of the hybrid cloud deployment landscape with precision and insight through vigilant performance monitoring and optimization. Chart a course towards operational excellence by continuously monitoring performance metrics, latency, and user experience post-migration. Leverage cloud-native monitoring tools and telemetry data to illuminate the darkest corners of your cloud kingdom, identifying bottlenecks, optimizing resource allocation, and optimizing the user experience to ensure a smooth and seamless journey to cloud enlightenment.
Employee Training and Education: Empowering Cloud Champions
Empower your legion of cloud champions with the knowledge, skills, and tools to conquer cloud migration challenges and thrive in the digital age. Provide comprehensive training and support programs to familiarize employees with cloud technologies, best practices, and governance frameworks. By nurturing a culture of continuous learning and innovation, organizations can cultivate a cadre of cloud evangelists equipped to champion the cause of digital transformation and propel the organization toward cloud excellence and competitive advantage.
Partner with Experts: Sailing with the Cloud Navigators
Set sail on the turbulent seas of cloud migration with the guidance and expertise of seasoned cloud navigators and wayfarers. Consider partnering with experienced cloud service providers or consultants to navigate the most aws cloud migration process smoothly and efficiently. By harnessing the wisdom and experience of cloud experts, organizations can chart a course towards success, avoiding treacherous shoals and navigating the complexities of cloud migration with confidence and competence.
Best Cloud Services Providers
In the vast expanse of cloud computing, navigating the myriad options can be daunting. However, with the top players in the industry, organizations can find their path to digital transformation illuminated. With the below cloud providers, organizations can reimagine what’s possible and embark on a journey of innovation and growth in the digital realm.

Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Comprehensive suite of cloud services, including computing, storage, database, machine learning, and IoT.
- Global infrastructure with regions and availability zones for high availability and low-latency connectivity.
- Advanced security features include AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and AWS Key Management Service (KMS).
- Scalable and flexible pricing models include pay-as-you-go, reserved, and spot instances.
Microsoft Azure
- Extensive portfolio of cloud services, including virtual machines, databases, AI, and blockchain.
- Hybrid cloud capabilities for seamless integration with on-premises infrastructure.
- Robust security features, including Azure Active Directory (AAD) and Azure Security Center.
- Integrated development tools and frameworks, such as Azure DevOps and Visual Studio.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Cutting-edge services for computing, storage, machine learning, and data analytics.
- Global network infrastructure with high-speed interconnectivity and edge computing capabilities.
- Built-in security controls, including Identity and Access Management (IAM) and GCP Security Command Center.
- Scalable and cost-effective solutions, with pricing options such as sustained and committed use discounts.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Cutting-edge services for computing, storage, machine learning, and data analytics.
- Global network infrastructure with high-speed interconnectivity and edge computing capabilities.
- Built-in security controls, including Identity and Access Management (IAM) and GCP Security Command Center.
- Scalable and cost-effective solutions, with pricing options such as sustained and committed use discounts.
IBM Cloud
- Comprehensive cloud offerings, including computing, storage, AI, and blockchain services.
- Enterprise-grade security features, including IBM Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) and data encryption.
- AI-powered automation tools for workload optimization and resource management.
- Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud capabilities, enabling seamless integration with on-premises environments.
Oracle Cloud
- Diverse cloud services, including compute, storage, database, and autonomous solutions.
- Integrated security controls, including Oracle Identity Cloud Service and Oracle Cloud Guard.
- High-performance computing infrastructure for demanding workloads and data-intensive applications.
- Comprehensive suite of developer tools and APIs for building and deploying cloud-native applications.
Conclusion
On premise to cloud migration represents a paradigm shift in how organizations manage their IT infrastructure and resources. While the transition may present challenges, the potential benefits of scalability, cost savings, and agility are too significant to ignore. By following best practices, addressing key considerations, and leveraging the expertise of cloud service providers, organizations can successfully navigate the cloud migration process and position themselves for future growth and innovation in the digital era.
FAQs
1. What is On-Premise to Cloud Migration?
On-premise to cloud migration refers to transferring data, applications, and workloads from local servers and infrastructure to remote cloud-based platforms.
2. How Does Cloud Computing Facilitate Migration Processes?
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure and services necessary for seamless migration. By offering computing resources, storage, and networking capabilities on-demand, cloud platforms empower organizations to execute migration tasks efficiently and scale their operations as needed.
3. What is a Data Migration Strategy in the Context of Cloud Migration?
The approach and methodologies for migrating data from on-premise environments to the cloud. This strategy encompasses decisions regarding data transfer methods, such as online cloud migration or offline data transfer, as well as considerations for data integrity, security, and compliance.
4. How Does Migrating Data to the Cloud Benefit Organizations?
Migrating data to the cloud unlocks numerous benefits for organizations, including enhanced scalability, improved accessibility, and reduced operational costs. Organizations can unlock insights, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries by centralizing data storage and leveraging cloud-based services for data processing and analytics.
5. What is an Online Cloud Migration, and How Does it Differ from Traditional Migration Methods?
Transferring data and applications to the cloud while they are still actively running in the on-premise environment.
