How Can MSys Expertise Help You with SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
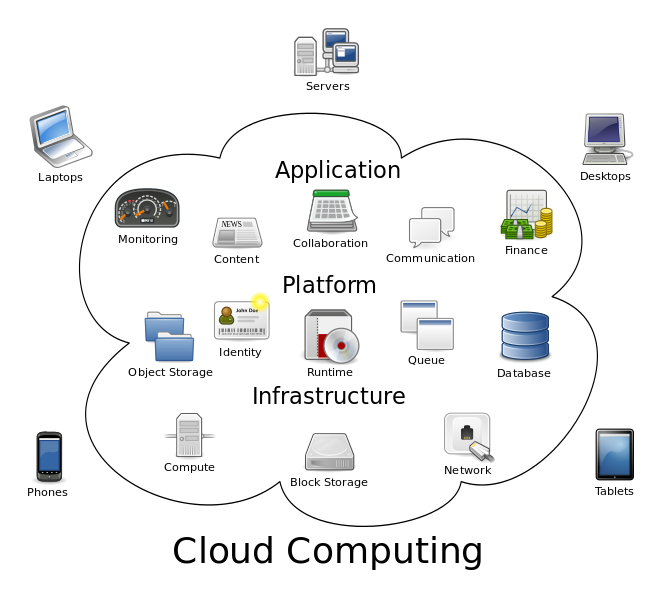
Cloud computing has revolutionized how we provide IT software and infrastructure. Today, many software companies are interested in providing their applications and services in the form of a cloud service rather than packaging their software and licensing it out to customers. There are a number of advantages to this type of service delivery model.
- Customers have access to applications and data from anywhere. Just a direct connection to the Internet is necessary for a cloud-based application to run. Data is also easily accessible over a network. Data would not be confined to a simple computer system or the internal network of an organization. Hence, access is easy from any location.
- Cost will come down in this model. You no longer need advanced hardware resources to run an application. A simple thin client can access a cloud-based application from anywhere. The hardware resources to run the application resides in the cloud, and it can be used to profitably run the application on any number of systems. The thin client can include a monitor, I/O devices, and just enough processing power to run the middleware that accesses the application from the cloud.
- Cloud computing systems are highly scalable. You don’t need to worry about adding additional hardware to run an application. The cloud takes care of all of that.
- Servers and storage devices take up a lot of physical space. Renting physical space can cost quite a lot of money for an organization. You can, with the cloud, simply host your products and software on someone else’s hardware so as to save a lot of space on your end.
- Streamlined hardware infrastructure of the cloud will have fewer technical support needs.
- Since cloud computing takes advantage of a grid computing system in the back end, the front end doesn’t really need to know the infrastructure to run any application of any size. In simpler terms, the advanced calculations a normal computer would take years to complete can be done in seconds through a cloud-computing platform.
Cloud Models
Cloud computing takes three major forms: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. They are expanded as Software, Platform, and Infrastructure as a Service. In the case of SaaS, users are given access to software applications and associated databases. The installation and operation of the software is done completely from the cloud, and the access through authentication is done from a thin client.
Cloud provides the load balancers required to run the application by distributing the work across multiple virtual machines. This complex back end is not even visible to the end user, who simply sees the running application through a single access point. The SaaS applications can be in subscription model, in which you pay a monthly or yearly fee to get access to the application.
In the PaaS model, the cloud provides a computing platform that includes typically an operating system (Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, etc.), programming languages required for software development, database, and web servers. These entities are all stored in the cloud. Instances of the PaaS model include Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine.
In the IaaS model, you have as many virtual machines as you need on the cloud. A hypervisor, such as VMware ESXi, Oracle VirtualBox, XenServer, or Hyper-V are provided through the IaaS platform. Additionally, virtual machine disk image library, raw block storage, object storage, firewalls, load balancers, virtual LANs, etc., are all provided by the IaaS model. This helps any organization successfully deploy their applications on the cloud. The most popular IaaS provider is probably Amazon Web Services.
Deployment Models
Three types of deployment models exist in the cloud architecture. They are private cloud, public cloud, and hybrid cloud. Private cloud is managed and operated by a single organization internally. Significant amount of virtualization is required for a private cloud deployment, and that can increase the initial investment required. However, when deployed correctly, a private cloud could be highly profitable for any organization.
Public cloud is rendered to the public as a service. For instance, Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, etc., are provided to the public to use and deploy their applications and infrastructure. This type of architecture requires you to analyze the security and communication concerns of the cloud.
In the case of hybrid cloud, as the name implies, both private, community, and public cloud deployments could be there. In hybrid cloud systems, the advantages of both types of systems may be there. Various deployment models are available in the case of hybrid cloud: for instance, a company can store sensitive client data in private cloud architecture while deploying business intelligence services provided by a public cloud vendor.
MSys’s Cloud Expertise
MSys and its subsidiary company Clogeny have done several cloud-based projects in the past. We have analyzed the current infrastructure of clients, and provided a proper road map to cloud deployment. In implementation, we have taken care of the complete design of the cloud computing model, building test environments to check the validity of the design, and migration of apps and data to go live. We also provide fully functional cloud support through transition plans, service review, and service implementations.
We have worked with some of the major cloud service providers in the industry including Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Rackspace, HP Cloud, Google Cloud, OpenStack, Salesforce, Google Apps, Netsuite, Office 365, etc. We have also helped organizations take advantage of their data by providing big data services. Leading companies in storage, server imaging, and datacenter provisioning have been our clients since our inception in 2007. In private and public cloud deployments, a few of our clients include Datapipe, Instance, and Netmagic.
Our cloud-based product is known as PurpleStrike RT, which is a load-testing tool that utilizes Amazon’s EC2 platform.
Conclusion
Cloud computing may prove to be the most important technology for future’s IT deployments. Already many companies have moved to the cloud. Many more are in the process of slowly transitioning to the cloud.
