Boost Your Success with the Potential of Observability in Complex IT Environments

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern IT, where complexity is the norm and rapid change is constant, the ability to gain deep insights and maintain a proactive stance is paramount. In this blog, we delve into the transformative potential of observability, exploring how it empowers businesses to not just survive but thrive amidst the challenges posed by complex IT environments.
Unveiling the Significance of Observability in Modern IT Systems
In today’s technology landscape, it is crucial for organizations to adopt a holistic approach towards understanding the intricate behavior of every component within their interconnected ecosystem of devices, networks, infrastructure, and applications. The complexity is further amplified by the distributed nature of these systems, driven by the ever-growing popularity of cloud computing. Consequently, businesses face challenges in obtaining a centralized view of resource utilization, efficiency, and performance. Additionally, the dynamic nature of IT systems, characterized by constant updates, reconfigurations, and installation of new packages, adds to the complexity, necessitating the adoption of observability.
What Makes Observability ‘The Watchful Protector’
- 81% of C-Suite executives expect to increase their observability budget in the next year with 20% expecting budgets to increase significantly.
- 90% believe observability is important and strategic to their business.
Observability empowers organizations to delve into the depths of their intricate and interconnected infrastructure, providing them with invaluable insights. By embracing observability, businesses can unlock a multitude of key aspects that facilitate enhanced understanding and management of their IT environments.
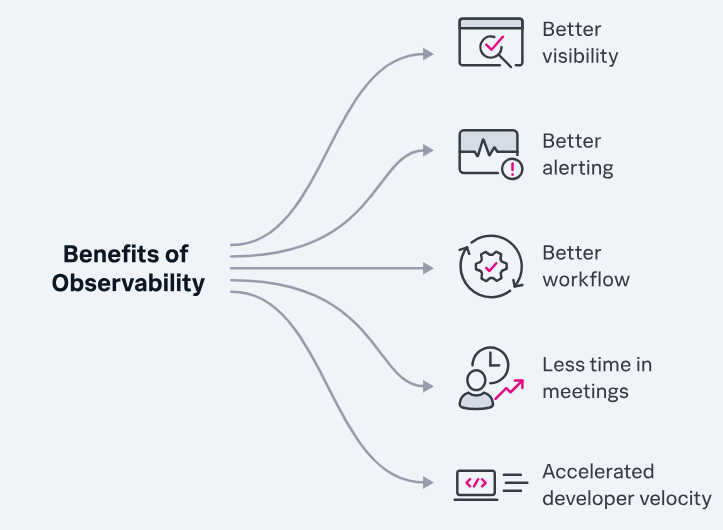
Image Source: Splunk
Let’s explore some of these crucial facets in greater detail:
- Real-time Monitoring: Observability provides real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing organizations to capture and analyze data as it happens. This enables proactive identification of issues and faster resolution.
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Observability involves collecting data from various sources, including logs, metrics, and traces. This comprehensive data collection provides a holistic view of the system, helping organizations understand the interdependencies between different components.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Once the data is collected, observability platforms employ advanced analytics and visualization techniques to make sense of the information. This helps in identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies, leading to better decision-making and troubleshooting.
- Cross-Domain Visibility: Observability breaks down the silos between different domains within an organization, such as development, operations, and security. It provides a unified view of the entire system, fostering collaboration and enabling teams to work together towards common goals.
- Adaptability and Scalability: With the ever-evolving nature of IT systems, observability solutions are designed to be adaptable and scalable. They can accommodate changes in the system architecture, handle increasing data volumes, and support the growth of the organization.
- Proactive Problem Resolution: By providing real-time insights into the system’s behavior, observability helps organizations proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact end-users. This leads to improved system reliability, performance, and customer satisfaction.
- Continuous Improvement: Observability promotes a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging organizations to analyze data, learn from it, and make informed decisions for optimizing their IT systems. It enables iterative enhancements and empowers organizations to stay ahead in a rapidly changing technological landscape.
What Observability has to offer (via Tools and Techniques)?
By providing a comprehensive view, proactive mitigation, and enhanced response capabilities, observability has the potential to greatly enhance overall system performance. While observability platforms provide an array of tools and technologies, here are some notable offerings that can improve the performance of IT systems in the following areas:
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Observability tools enable organizations to collect a wide range of data, including logs, metrics, traces, and events. This comprehensive data collection provides a holistic view of the system and allows for in-depth analysis and troubleshooting.
- Real-time Monitoring: Observability tools provide real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing organizations to monitor their systems continuously. This enables prompt detection of issues, faster response times, and proactive problem resolution.
- Visualization: Observability tools often include visualization capabilities, presenting data in a visual format such as charts, graphs, and dashboards. This visualization aids in understanding complex system behaviors and facilitates quick decision-making.
- Alerts and Notifications: Observability tools can be configured to generate alerts and notifications based on predefined thresholds or conditions. This helps organizations stay informed about critical events or deviations from normal system behavior, enabling them to take immediate action.
- Cross-domain Integration: Observability techniques promote cross-domain integration by breaking down the silos between different teams and departments within an organization. By providing a unified view of the system, observability tools facilitate collaboration and communication among various stakeholders.
- Distributed Tracing: Observability techniques, such as distributed tracing, allow organizations to trace the path of requests through different components of a system. This tracing capability helps pinpoint bottlenecks, latency issues, and dependencies, aiding in performance optimization.
- Automated Remediation: Some advanced observability tools offer automated remediation capabilities. These tools can automatically detect and address certain issues, reducing manual intervention, and improving system uptime and reliability.
The role, significance, and relevance of observability platforms in the present era cannot be overstated. With the increasing complexity of IT systems characterized by distributed architectures, cloud computing, and interconnected infrastructures, observability has become a strategically important tool with profound implications for system performance and organizational profitability. In essence, organizations aiming to be at the forefront of their industries must prioritize observability as a fundamental aspect to optimize performance and proactively meet the evolving needs of their target markets, thus securing a competitive advantage.
