14 Essential Steps for Oracle 12c Load Testing using SLOB on All-Flash Block Storage

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
Testing – whether QA Automation services, testing accelerators or test automation tools, require hands on expertise and deep knowledge. The purpose of this blog is to document on how SLOB can be used for load testing on Oracle 12c database. The guide is specific to Oracle 12c using SLOB on CentOS 7.4.
Configuration used:
Below is the setup we used for experimenting Oracle12c using SLOB.
VM (ESXi) with CentOS release 7.4.x installed (Stand-alone setup)
Below are the versions of software used:
- OS version : Centos 7.4.1708
- Oracle 12c: Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.2.0.1.0 – 64bit
- SLOB version: Slob_2.4.2.1
Prerequisites:
Below are some the prerequisites before we proceed for Oracle 12c and SLOB installation.
- Yum package management application must be installed.
- Root or sudo access to the install machines.
- At-least 2GB of RAM.
Oracle 12c Installation:
Oracle database is one of the most widely used relational database management systems (RDBMS) in enterprise environments. Developed, maintained, and supported by Oracle Corporation.
This section covers 14 key steps on how can you setup and install Oracle 12c Release 2 on CentOS 7 VM.
Setting up Oracle 12c on ESXi VM running CentOS 7
Step 1 – Install required Packages
Installation of several packages required by Oracle database, like GCC, Binutils, Glibc etc. Hence we will install them from the Centos repository using yum command. Install packages required by Oracle database with yum
yum update -y yum install -y binutils.x86_64 compat-libcap1.x86_64 gcc.x86_64 gcc-c++.x86_64 glibc.i686 glibc.x86_64 glibc-devel.i686 glibc-devel.x86_64 ksh compat-libstdc++-33 libaio.i686 libaio.x86_64 libaio-devel.i686 libaio-devel.x86_64 libgcc.i686 libgcc.x86_64 libstdc++.i686 libstdc++.x86_64 libstdc++-devel.i686 libstdc++-devel.x86_64 libXi.i686 libXi.x86_64 libXtst.i686 libXtst.x86_64 make.x86_64 sysstat.x86_64 zip unzip smartmontools [root@oracledb ~]# cat /etc/hosts 10.20.178.69 oracledb
Step 2 – Configure User and System
Create new groups named ‘oinstall‘ and ‘dba‘, then create a new user ‘oracle‘ and add it to the ‘oinstall’ group.
groupadd oinstall groupadd dba useradd -g oinstall -G dba oracle passwd oracle TYPE THE PASSWORD
Edit ‘sysctl.conf‘ file with vim & update the below details,
vim /etc/sysctl.conf fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576 fs.file-max = 6815744 kernel.shmall = 2097152 kernel.shmmax = 2147483648 kernel.shmmni = 4096 kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65500 net.core.rmem_default = 262144 net.core.rmem_max = 4194304 net.core.wmem_default = 262144 net.core.wmem_max = 1048586
Save the file and exit the editor.
Now run the commands below to display all kernel parameter and apply the new values.
sysctl -p sysctl -a
Edit ‘limits.conf‘ file with vim. Update the below & save the file and exit the editor.
vim /etc/security/limits.conf oracle soft nproc 2047 oracle hard nproc 16384 oracle soft nofile 1024 oracle hard nofile 65536 oracle soft stack 10240
Step 3 – Configure Desktop
Install X Window System with yum command below.
yum groupinstall -y "X Window System"
When the installation is done, open a new terminal and connect to the server as oracle user with the ssh command option below
ssh -X [email protected]
Step 4 – Download Oracle Database
If you do not have an Oracle account yet, register one and then login to download Oracle 12c for Linux.
Below are my oracle files,
[root@oracledb ~]# mkdir ~/oracle [root@oracledb ~]# cd ~/oracle/ [root@oracledb oracle]# ll total 3372752 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3453696911 May 13 14:25 linuxx64_12201_database.zip
Extract the Oracle files to a new directory named ‘stage‘.
[root@oracledb oracle]# unzip linuxx64_12201_database.zip -d /stage/
Change owner and group of the ‘/stage/’ directory to the oracle user and oinstall group.
[root@oracledb oracle]# chown -R oracle:oinstall /stage/
Step 5 – create new directories for the Oracle installation files and Oracle database files
Storage Configuration: Created 2 vdisks of 100GB, 1TB on CentOS 7 VM - ESXi Datastore created using Storage volume. fdisk /dev/sdb - 100G fdisk /dev/sdc - 1TB mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdb1 mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdc1 mkdir -p /u01 /u02 mount /dev/sdb1 /u01 mount /dev/sdc1 /u02 [root@oracledb ~]# cat /etc/fstab /dev/sdb1 /u01 xfs defaults 0 0 /dev/sdc1 /u02 xfs defaults 0 0
Directory ‘/u01‘ is for the Oracle installation files and ‘/u02‘ for the Oracle database files.
Change owner and group of the new directories and set permissions to ‘755’.
[root@oracledb ~]# chown -R oracle:oinstall /u01 /u02 [root@oracledb ~]# chmod -R 775 /u01 /u02 [root@oracledb ~]# chmod g+s /u01 /u02
Oracle is downloaded and the new directories for the installation are ready.
Step 6 – Install Oracle Database 12c
Open a new terminal and connect to the CentOS 7 server using the oracle user with the ssh command below.
ssh -X [email protected] Go to the stage database directory and run the installer file. [oracle@oracledb ~]$ cd /stage/database/ [oracle@oracledb database]$ ./runInstaller Starting Oracle Universal Installer... Checking Temp space: must be greater than 500 MB. Actual 37229 MB Passed Checking swap space: must be greater than 150 MB. Actual 3967 MB Passed Checking monitor: must be configured to display at least 256 colors. Actual 16777216 Passed Preparing to launch Oracle Universal Installer from /tmp/OraInstall2019-05-16_02-59-35PM. Please wait ...[oracle@oracledb database]$
And you will see the GUI installation screen below, there click ‘Next‘.
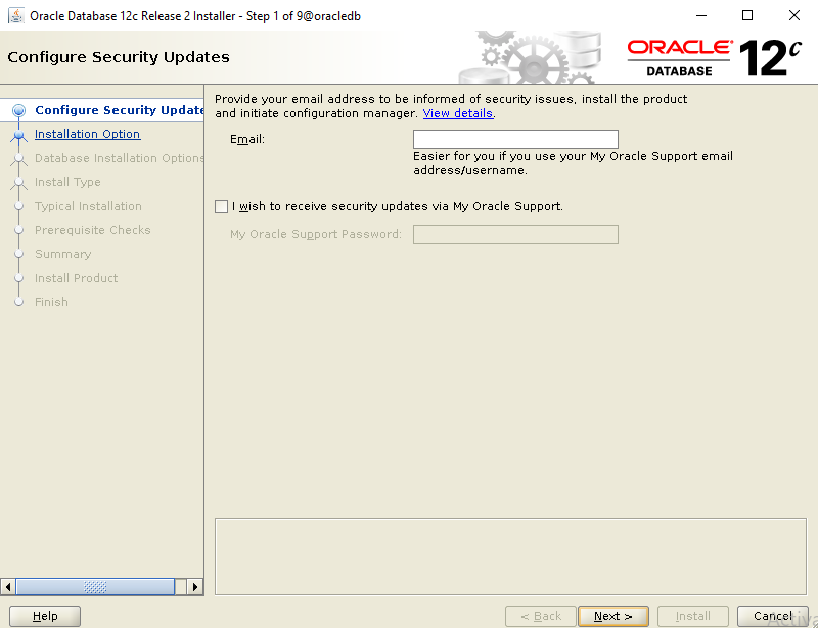


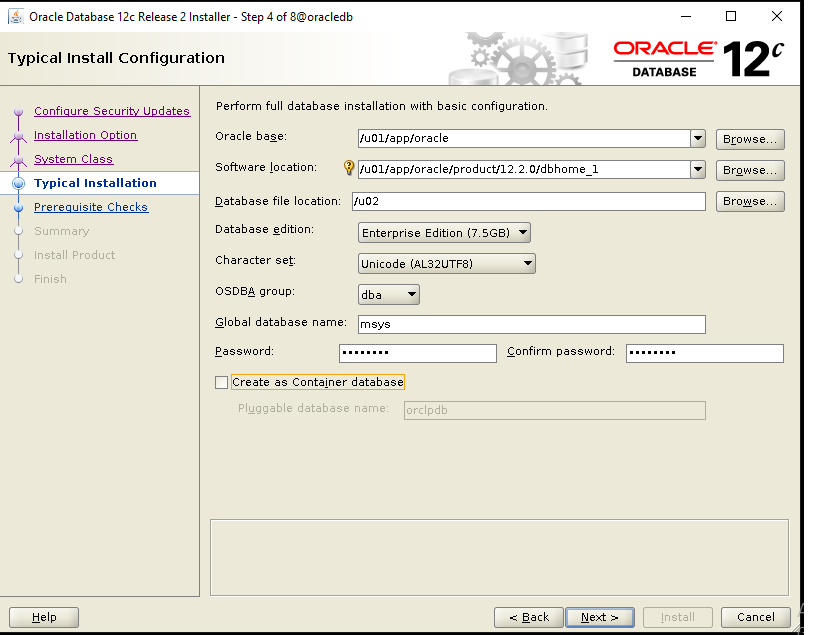
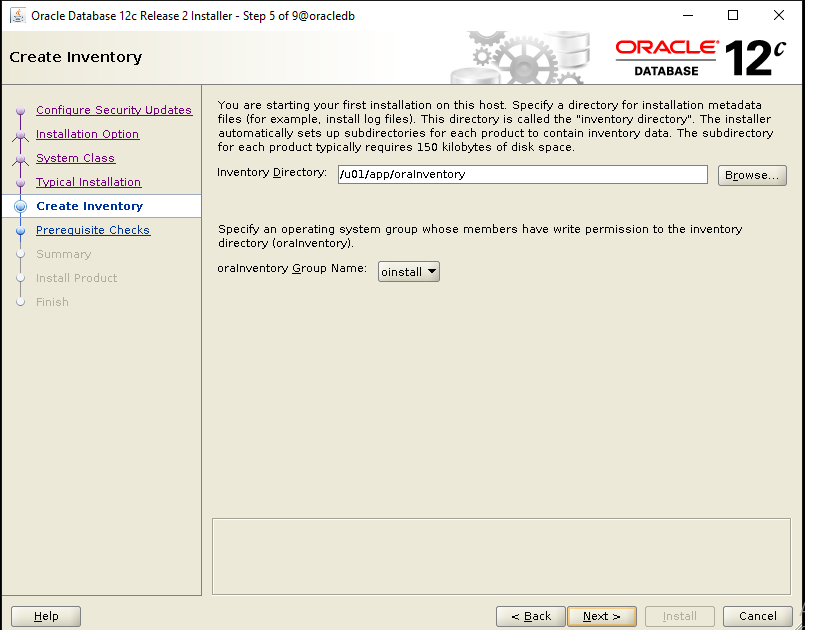
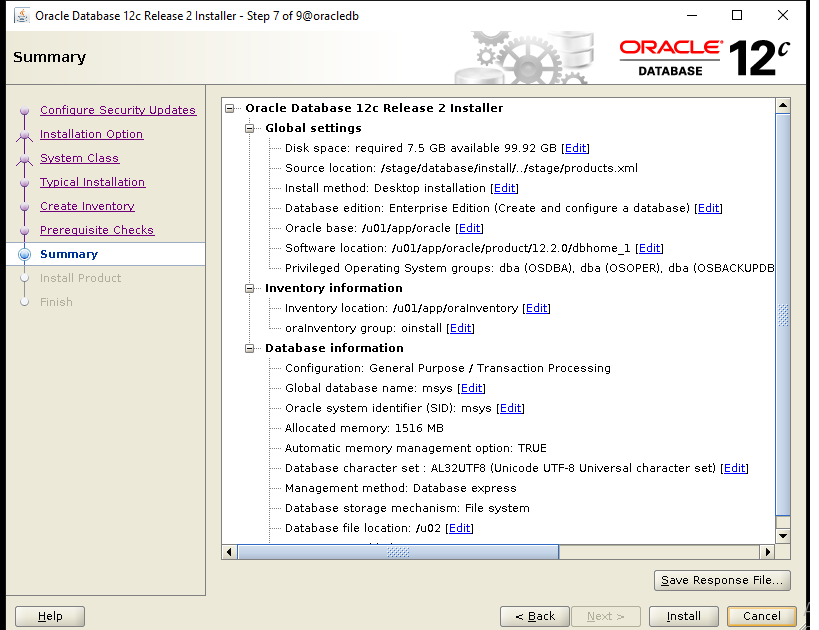

During installation process, you will be asked to execute some scripts as root.
[root@oracledb ~]# cd /u01/app/oraInventory/ [root@oracledb oraInventory]# ./orainstRoot.sh Changing permissions of /u01/app/oraInventory. Adding read,write permissions for group. Removing read,write,execute permissions for world. Changing groupname of /u01/app/oraInventory to oinstall. The execution of the script is complete. [root@oracledb ~]# cd /u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/ [root@oracledb dbhome_1]# ./root.sh Performing root user operation. The following environment variables are set as: ORACLE_OWNER= oracle ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1 Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]: Copying dbhome to /usr/local/bin ... Copying oraenv to /usr/local/bin ... Copying coraenv to /usr/local/bin ... Creating /etc/oratab file... Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created Finished running generic part of root script. Now product-specific root actions will be performed. Do you want to setup Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA) now ? yes|[no] : no Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA - User Mode) is available at : /u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/suptools/tfa/release/tfa_home/bin/tfactl OR Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA - Daemon Mode) can be installed by running this script : /u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/suptools/tfa/release/tfa_home/install/roottfa.sh
Click ‘Close‘.
Step 7 – Testing
The Oracle installation is finished and ready for testing. I will try to access Oracle from the command line first (sqlplus)
Log in to the server and access the oracle user.
[root@oracledb ~]# su - oracle
Add the following lines to .bash_profile file
[oracle@oracledb ~]$ cat .bash_profile # .bash_profile # Get the aliases and functions if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then . ~/.bashrc fi # User specific environment and startup programs export ORACLE_SID=msys export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1 export PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH Reloading .bash_profile to apply the new settings [oracle@oracledb ~]$ source .bash_profile Note: Exit out of the terminal & re-login as oracle user.
Testing to make sure Sqlplus is working fine.
[oracle@oracledb ~]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 12.2.0.1.0 Production on Thu May 16 16:33:48 2019 Copyright (c) 1982, 2016, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.2.0.1.0 - 64bit Production SQL>
Next, try to access the web-based ‘Oracle Enterprise Manager‘. Open your web browser and type the https URL below on port 5500. Use the IP of your server!
https://10.20.178.69:5500/em/
Login with user ‘system‘, and the password you have setup as ‘Administrative Password‘ in step 6 Pic4.
Note:
When web browser is not accessible, need to allow connections from outside the server, you will need to open the following ports:
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=1521/tcp --add-port=5500/tcp --add-port=5520/tcp --add-port=3938/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload

After login, you will see the ‘Oracle Enterprise Manager’ dashboard below.
The Oracle Database 12c installation and configuration is done.
Oracle database utility and Oracle Enterprise manager are working.
Step 8 – Installing SLOB [The Simple Database I/O Testing Toolkit for Oracle Database]
Download the latest SLOB package from the below link.
https://kevinclosson.net/slob/
Extract the file using oracle user and continue to use oracle user to setup SLOB,
[oracle@oracledb ~]$ ls 2018.04.16.slob_2.4.2.1.tar.gz [oracle@oracledb ~]$ tar xvzf 2018.04.16.slob_2.4.2.1.tar.gz [oracle@oracledb ~]$ ls 2018.04.16.slob_2.4.2.1.tar.gz SLOB
[oracle@oracledb ~]$ cd SLOB/wait_kit/ [oracle@oracledb wait_kit]$ make all rm -fr *.o mywait trigger create_sem cc -c -o mywait.o mywait.c cc -o mywait mywait.o cc -c -o trigger.o trigger.c cc -o trigger trigger.o cc -c -o create_sem.o create_sem.c cc -o create_sem create_sem.o cp mywait trigger create_sem ../ rm -fr *.o
Step 9 – SLOB Configurations
Setup already has Database created in the name“msys” (per step 6 – Pic4 above). Configure the slob.conf file which is located in the SLOB directory
#### SLOB 2.4.0 slob.conf - sample file I used UPDATE_PCT=50 <== 100% read (0% update), 70/30 read/write (30% update), 50/50 read/write (50% update) SCAN_PCT=0 RUN_TIME=172800 <== count in seconds that SLOB will run WORK_LOOP=0 SCALE=8G SCAN_TABLE_SZ=1M WORK_UNIT=64 REDO_STRESS=HEAVY LOAD_PARALLEL_DEGREE=2 SQLNET_SERVICE_BASE=msys <== mention the database name SYSDBA_PASSWD="Passw0rd" <== Administrative Password' created in step 6 Pic4.
Step10: Create tablespaces in MSYS database.
[oracle@oracledb ~]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 12.2.0.1.0 Production on Thu May 16 16:55:56 2019 Copyright (c) 1982, 2016, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.2.0.1.0 - 64bit Production SQL> select instance_name, instance_role, database_status from v$instance; INSTANCE_NAME INSTANCE_ROLE DATABASE_STATUS ---------------- ------------------ ----------------- msys PRIMARY_INSTANCE ACTIVE SQL> create bigfile tablespace slobdata datafile '/u02/msys/slobdata.dbf' size 128G autoextend on; Tablespace created.
Step11: Create Database Users and Object for SLOB using user oracle
Note: In this example we are creating 128 SLOB schemas, each with 8GB of data. The size of each schema is controlled by the SCALE parameter in the slob.conf file. 128 8GB schemas will yield 1TB of test data.
[oracle@oracledb SLOB]$ ./setup.sh SLOBDATA 128 SLOB 2.4.0 NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:31 : NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:31 : Begin SLOB setup. NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:31 : ADMIN_CONNECT_STRING: "system/Passw0rd" NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:31 : Load parameters from slob.conf: SCALE: 8G (1048576 blocks) SCAN_TABLE_SZ: 1M (128 blocks) LOAD_PARALLEL_DEGREE: 2 ADMIN_SQLNET_SERVICE: "" SYSDBA_PASSWD: "Passw0rd" DBA_PRIV_USER: "system" Note: setup.sh will use the following connect strings as per slob.conf: Admin Connect String: "system/Passw0rd" Non-Admin Connect String: " " NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:31 : Testing Admin connect using "sqlplus -L system/Passw0rd" NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:32 : Dropping prior SLOB schemas. This may take a while if there is a large number of old schemas. NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:32 : Previous SLOB schemas have been removed NOTIFY : 2019.05.16-17:40:32 : Preparing to load 128 schema(s) into tablespace: SLOBDATA NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-07:12:18 : Loading user1 schema NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-07:22:42 : Finished loading, indexing and gathering statistics on user1 schema in 624 seconds NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-07:22:42 : Commencing multiple, concurrent schema creation and loading NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-07:22:43 : Waiting for background batch 1. Loading up to user3 Output EOL: NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:57:04 : Waiting for background batch 64. Loading up to user128 NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:00 : Finished background batch 64. Load / index create / stats gather in 116 seconds NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:00 : Completed concurrent data loading phase: 9378 seconds NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:00 : Creating SLOB procedure NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:01 : SLOB procedure created NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:01 : Row and block counts for SLOB table(s) reported in ./slob_data_load_summary.txt NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:01 : Please examine ./slob_data_load_summary.txt for any possbile errors NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:01 : NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:01 : NOTE: No errors detected but if ./slob_data_load_summary.txt shows errors then NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:01 : examine /home/oracle/SLOB/cr_tab_and_load.out NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-09:59:01 : SLOB setup complete. Total setup time: (10004 seconds)
Step12: Install STATSPACK as SLOB will need to use it.
The script is located at ~$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin
SQL> @/u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/rdbms/admin/spcreate.sql Session altered. Choose the PERFSTAT user's password ----------------------------------- Not specifying a password will result in the installation FAILING Enter value for perfstat_password: Passw0rd Passw0rd Choose the Default tablespace for the PERFSTAT user --------------------------------------------------- Below is the list of online tablespaces in this database which can store user data. Specifying the SYSTEM tablespace for the user's default tablespace will result in the installation FAILING, as using SYSTEM for performance data is not supported. Choose the PERFSTAT users's default tablespace. This is the tablespace in which the STATSPACK tables and indexes will be created. TABLESPACE_NAME CONTENTS ------------------------------ --------------------- STATSPACK DEFAULT TABLESPACE ---------------------------- SLOBDATA PERMANENT SYSAUX PERMANENT *USERS PERMANENT Pressing <return> will result in STATSPACK's recommended default tablespace (identified by *) being used. Enter value for default_tablespace: SLOBDATA Using tablespace SLOBDATA as PERFSTAT default tablespace. Choose the Temporary tablespace for the PERFSTAT user ----------------------------------------------------- Below is the list of online tablespaces in this database which can store temporary data (e.g. for sort workareas). Specifying the SYSTEM tablespace for the user's temporary tablespace will result in the installation FAILING, as using SYSTEM for workareas is not supported. Choose the PERFSTAT user's Temporary tablespace. TABLESPACE_NAME CONTENTS DB DEFAULT TEMP TABLESPACE ------------------------------ --------------------- -------------------------- TEMP TEMPORARY * Pressing <return> will result in the database's default Temporary tablespace (identified by *) being used. Enter value for temporary_tablespace: Using tablespace TEMP as PERFSTAT temporary tablespace. Output EOL: Package created. No errors. Creating Package Body STATSPACK... Package body created. No errors. NOTE: SPCPKG complete. Please check spcpkg.lis for any errors.
Step13: Starting SLOB test
To run SLOB, we use the runit.sh script in the SLOB directory. In this example I am going to use all of the 128 schemas I created, and specify one thread per schema:
[oracle@oracledb SLOB]$ ./runit.sh -s 128 -t 1 NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-10:18:21 : Test has been triggered. Processes are executing. NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-10:18:21 : List of monitored sqlplus PIDs written to /tmp/.SLOB.2019.05.17.101722/18481.f_wait_pids.out. NOTIFY : 2019.05.17-10:18:31 : Waiting for 172787 seconds before monitoring running processes (for exit). NOTIFY : 2019.05.20-14:49:09 : SLOB test is complete. NOTIFY : 2019.05.20-14:49:09 : Cleaning up SLOB temporary directory (/tmp/.SLOB.2019.05.20.141756).
Step14: We can inspect this AWR report to see the I/O observed by Oracle.
You can run AWR reports to see statistics about database performance. Log in with SQLPlus and run:
@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrrpt.sql
Example below:
[oracle@kubeworker2 SLOB]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 12.2.0.1.0 Production on Mon May 20 16:09:32 2019 Copyright (c) 1982, 2016, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.2.0.1.0 - 64bit Production SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/awrrpt.sql Type Specified: html Final EOL output: Report written to awrrpt_1_1_7.html
The above HTML file can be opened in web browser
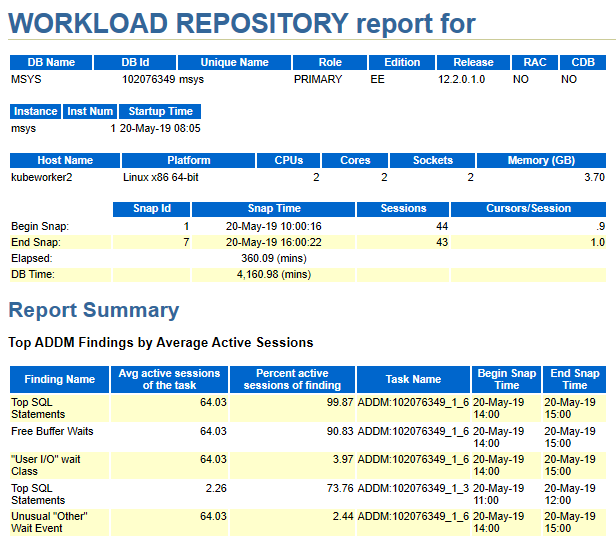
Conclusion:
SLOB is a great tool for testing Oracle DB I/O performance.
Created and tested with enough data to exceed the database and stress the array performance.
Use AWR to see what Oracle DB observed as I/O performance.
References:
https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-oracle-database-12c-on-centos-7/
https://gruffdba.wordpress.com/2017/03/04/testing-emc-unity-storage-performance-with-slob/
